Algorithms: Selection sort (JavaScript, PHP)
- Time complexity: O(n2)
Hi, in the second episode of the algorithms series I’d like to take a closer look at yet another simple sorting technique called selection sort. Similarly to bubble sort, it consists of two dependent loops, therefore it’s time complexity also equals to O(n2). It goes like this:
- While sorting the array in ascending order we set the first loop and the first element in the array as a minimum.
- We set up a second loop with a range of the second till the last element, as it doesn’t make much sense to compare the first element with itself.
- If any of the remaining elements in the array is lower than the first, we set it as a minimum.
- As a final step, the lowest value is swapped with the first value (at 0 index).
- The loop continues with j+1 element as a minimum and j+1+1 as the remaining range.
Here’s the presentation (credits to http://www.xybernetics.com):
Algorithms: Bubble sort (JavaScript, PHP)
- Time complexity: O(n2)
Bubble sort is one of the easiest sorting algorithms to implement. The name is derived from the process of sorting based on gradually “bubbling” (or rising) values to their proper location in the array. The bubble sort repeatedly compares adjacent elements of an array as in the following picture:
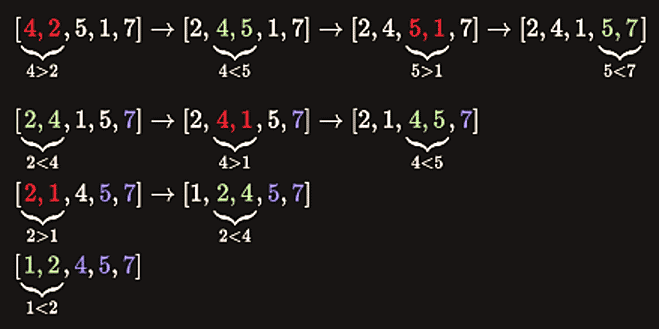
The first and second elements (4 and 2) are compared and swapped if out of order. Then the second and third elements (4 and 5) are compared and swapped if out of order and so on. The algorithm consists of two loops. In each iteration a single value is set in the right place. This sorting process continues until the last two elements of the array are compared and swapped if out of order (the last iteration doesn’t swap any values).
